Introduction:
Serum folate (SF), vitamin B12 (B12), and iron deficiency (def) are common causes of nutritional anemias (NA). These deficiencies are usually multifactorial, with nutritional and non-nutritional causes playing a role. SF, B12, and iron levels are usually ordered in the setting of anemia, and malnutrition with or without neurologic symptoms. Clinical evidence suggests that these def have a strong dietary component and socioeconomic status (SES). The relationship of NA and area-based SES in the US has not been studied. We aimed to determine the relationship of SES with the prevalence of NA.
Methods:
We performed a cross-sectional analysis of adult patients with SF, B12 and iron levels at Mayo Clinic Arizona and Florida between 2010 and 2018.
Race was classified using the NIH criteria. Normal laboratory values were determined according to our lab reference and the US NHANES III. SF levels (mcg/Lt) were defined as deficient <4, normal ≥4.0, and excess ≥20. B12 levels (ng/L) as deficient <150, borderline 150-400, normal >400-900, and excess ≥900. Iron def was determined by ferritin levels (mcg/L) as low <24, normal 24-336, elevated >336 for men, low <11, normal 11-307, elevated >307 for women. Area-Level SES indicators: Median Household income (MHI), unemployment rate (UR), median gross rent month (MGRM), % uninsured, median house value (MHV), % high school; were geocoded by zip code using the 2014 American Community Survey. Demographics and clinical variables were compared between groups by chi-square test for frequency data or Kruskal Wallis rank-sum test for continuous variables.
Results:
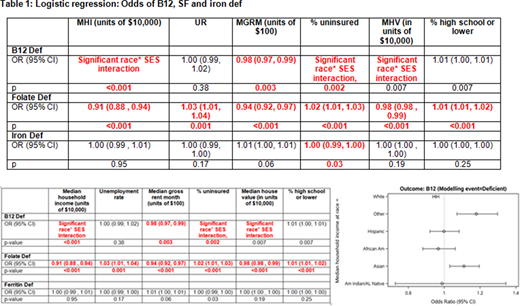
202,046 samples from 128,084 patients were analyzed. In the sample-level analysis, there were statistically significant associations between SES and SF def; all SES indicators except UR for B12 def; and no differences for iron def, except % uninsured (Table 1). There was no statistically significant interaction between race and SES for SF def and iron def. Race was a statistically significant modifier between B12 def and MHI (p<0.001), % uninsured (p=0.002), and MHV (p=0.007). Asian and Other race had an increase in odds of B12 def with increasing MHI (Asian OR=1.11 , Other OR=1.18); white race had a decrease in odds of B12 def with increasing MHI (OR=0.95 for a $10,000 increase in MHI).
Conclusions:
We show significant relationships between SES and NA in the US. Differences were observed between SF def and all the SES indicators without race interactions. There were significant interactions between B12 def, race and SES for pts of White, Asian and Other race. There were no differences between SES and race for iron def. These relationships confirm that NA are related to area-level SES and other social determinants of health. Research regarding the causes of these disparities on a population level are needed.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract